Photogrammetry is the science of applying mathematics to photographs for the purpose of extracting accurate 3D measurements. The word photogrammetry is a concatenation of the words “photo” (light), “gram” (record), and “metry” (measurement). The original methodology first showed up as artists began to create more realistic paintings all the way back in the 14th century.

History
The concept of measuring pictures dates back all the way to the Renaissance. As artists would strive to generate realism in their works, they began to understand the application of mathematics could improve paintings by more accurately representing the subject of their works. These formulas and methods would continue to be refined and improved all the way up to the invention of the camera around the turn of the 19th century. The combination of these concepts and the accuracy of photography allowed photogrammetry to become more widely used as a tool for measurement.
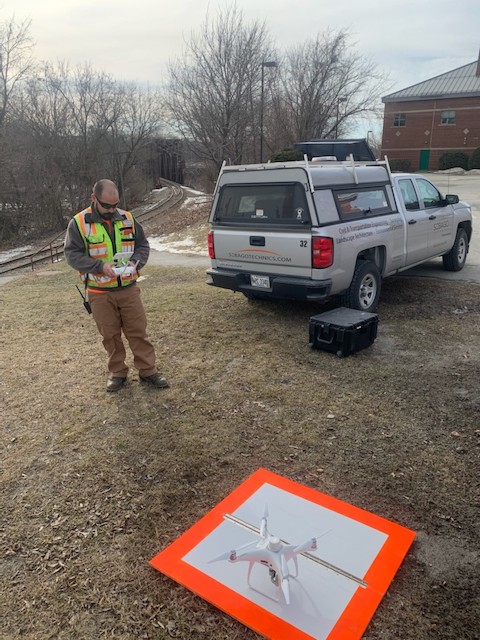

Types of Photogrammetry
In the practice of photogrammetry there are two main methods for collecting photographs. Pictures can be taken on traditional tripods set on the ground; this is known as terrestrial photogrammetry. By taking multiple overlapping photos, objects can be measured stereoscopically in three-dimensions. With the development of drone technology, photographs can also be taken in the sky. Affixing a camera to the bottom of an aerial vehicle allows high-resolution images to be collected across hundreds or thousands of feet. This method of photo collection is known as aerial photogrammetry. Each method can be utilized individually or jointly depending on the needs of the project or task.
Aerial photogrammetry is generally utilized on large or difficult to access sites and can cover large areas quickly while terrestrial photogrammetry is more object-focused. The scale of the project will determine the best methodology for a photograph collection.
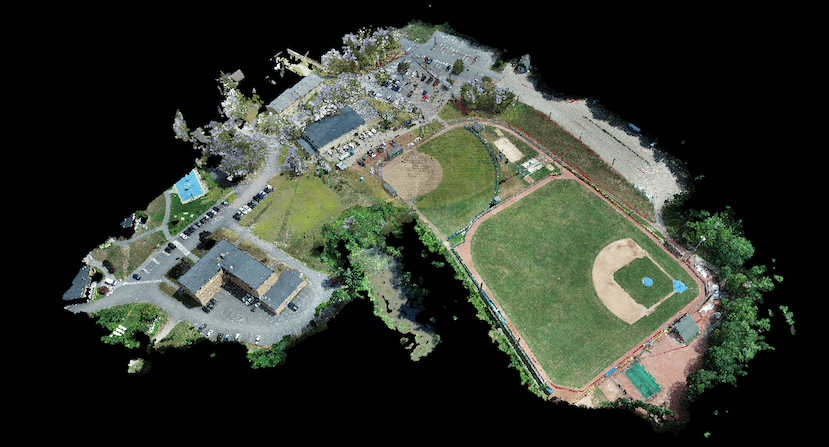

What is Produced by Photogrammetry?
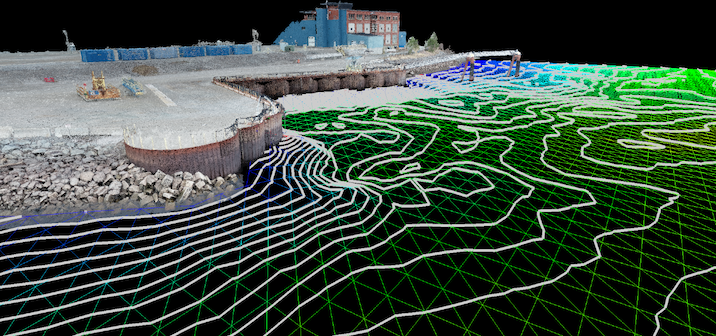
The measurements produced by this method can be utilized to generate orthorectified aerial images for use in drafting software such as AutoCAD or fully three-dimensional point clouds for use in modeling software such as Revit and Cyclone. These datasets and images act as the base for the existing conditions of an object or site that will be utilized during the information gathering, surveying, and design processes of a project.
Why is it used?
The plans and models produced by photogrammetry are necessary for use by design professionals and surveyors by accurately measuring the world around us. No matter the scale of a project, the versatility of photogrammetry allows the data to be collected accurately. Civil engineers utilize this technology for grade surfacing and site inspection, while digital modelers leverage datasets to model statues and building details. During the first Apollo landing, satellite images were used to safely determine a landing zone on the surface of the moon. The development of this technology has produced tools that greatly speed up data collection and accuracy, helping professionals to perform their work more quickly and correctly.

Want to learn more about Sebago Technics’ aerial photogrammetry services? Contact Brian Williams, PLS (207-200-2130) to discuss your project needs.

